People’s Daily: “the Silk Road on ice” attracts the world’s attention

- Date: Jan 30, 2018
- Comments: no comments
- Categories: News
“China is willing to rely on the development and utilization of the Arctic waterway to work with all parties to establish the Silk Road on Ice.” On January 26, the Chinese government published the first white paper on the policy of the Arctic – the “Arctic Poverty Policy in China” The formulation of the “Ice Silk Road” has aroused great concern in the world.
“China Announces Plan for the Arctic Silk Road,” the BBC said in the same day’s report that China and the Arctic countries like Russia will jointly develop the Arctic channel. This is an “ambitious change in China-Europe and other land-sea ties.” Part of the grand plan “that will give China access to a transport route closer to ports in other countries than through the Suez Canal and the Panama Canal. “From the oil and gas to expanding the Belt and Road initiative, China has expressed its readiness to promote international cooperation in the Arctic,” said United Press International. Today’s Russian news agency article holds that the white paper reflects China’s attitude toward Arctic cooperation around the world.
The Arctic waterway will dramatically change the global shipping pattern
“To carry out Arctic waterway cooperation and work together to build the ‘Silk Road on Ice,’ implement the project of interconnection and interoperability.” Chinese President Xi Jinping met with Russian Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev in Moscow in July last year. When meeting with Medvedev in Beijing four months later, President Xi Jinping once again expressed his willingness to work together on the development and utilization of the Arctic waterway to create the “Silk Road on Ice.”
China proposed building a “ice-silk road” with historical and realistic foundations. Since joining the Treaty of Spitsbergen in 1925, China’s exploration of the North Pole has been deepened, its practices continuously expanded, its activities expanded and its cooperation deepened. In recent decades, with the global warming, the development and utilization of the Arctic channel historic opportunity. China has proposed the “One Belt and One Road” initiative and continuously promoted the interconnection and interconnection among all countries. It naturally became an advocate and active promoter of the “ice-silk road.”
“The opening of the Arctic Waterway will promote the overall growth of the circular Arctic economy and make major changes in the global trade and shipping pattern.At the present Arctic economic opportunities have increased but infrastructure construction is weak with a huge gap and there is a great demand for the Chinese market, capital and technology Yang Jian, vice president of Shanghai Institute of International Studies, told this reporter that the Chinese government advocates multi-party cooperation to jointly build the Arctic Ice Silk Road and focuses on economic cooperation in the Arctic waterway and energy cooperation and development Forward-looking investment, efforts to contribute to the Arctic infrastructure and digital construction.
Arctic waterways include the Northeast Passage, the Northwest Passage and the Central Passage. Russia invites the northeast waterway co-constructed with China to start from the northwestern part of northwestern Europe to the east of Vladivostok via the Barents Sea, the Kara Sea, the Laptev Sea, the Novosibirsk Sea and the Bering Strait, Is the shortest sea route connecting Northeast Asia and Western Europe.
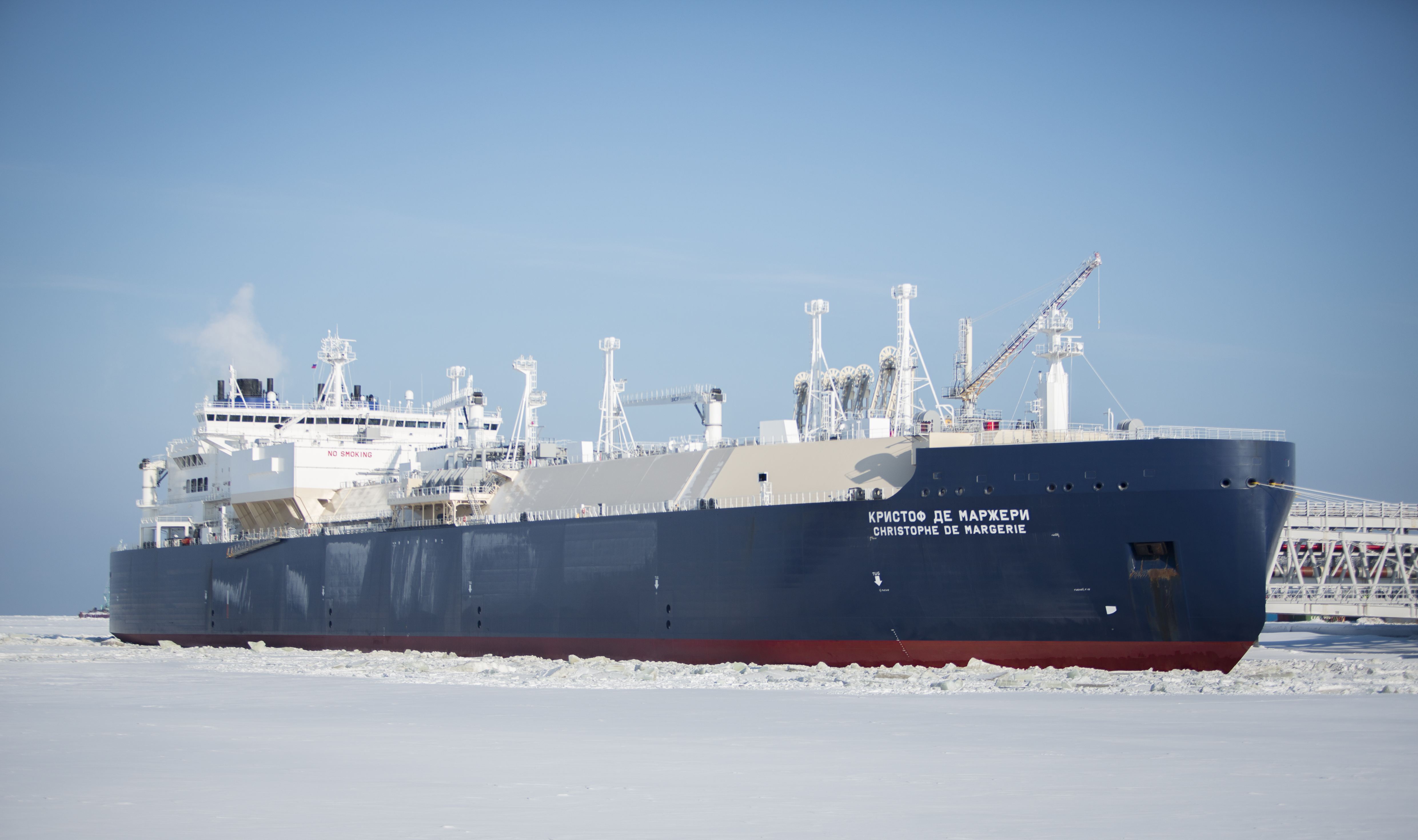
In 2013, COSCO SHIPPING’s “Insein” vessel sailed for the first time on this waterway as a Chinese freighter. Up to now, COSCO Shipping Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of COSCO SHIPPING Group, has dispatched 10 vessels to the northeast channel of the Arctic to carry out 14 voyage missions. Among them, the five vessels in 2017 mainly carry cargoes such as equipment, steel and pulp, and explore the normalization and operation of the north-east fairway of the Chinese commercial shipping.
Chen Feng, general manager of COSCO Shipping Finland, said COSCO Shipping Finland is investigating the possibility of normalizing services in the Arctic shipping channel. The Northeast Passage saves time and mileage compared to traditional routes and is becoming a new route linking East Asia and Europe. The commercial potential of developing this route has become a new target for COSCO Shipping Finland.
The BBC reported that it took only 20 days to travel from China to Rotterdam via the Arctic Passage, and that the Suez Canal to Rotterdam now requires 48 days to sail. According to data from the Arctic Logistics Center in Russia, a total of 297 vessels sailed through the Arctic north-eastern channel in 2016, an increase of 35% over the previous year. Industry insiders predict that with the accelerated melting of Arctic sea ice, the number of ships connecting China, Russia and Central Europe to the northeast fairway will increase year by year.
The cooperation between China and Russia in developing the Arctic has made positive progress
Russia’s Economic News Agency today quoted Alexander Pyativa, director of Russia’s North and Arctic Economic Center, as saying that China’s Arctic policy is to work with all countries to jointly build the “Silk Road on Ice,” so that enterprises can participate in infrastructure construction. Pyithiasov believes that in recent years China’s important grip on developing its foreign relations is the Belt and Road Initiative. The Silk Road on Ice is an important part of the Belt and Road Initiative.
As early as 2015, Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov once said that China is one of Russia’s top partners in Arctic cooperation. At the annual press conference held in December last year, Russian President Putin formally invited China to participate in the construction of the Arctic traffic corridor and build the “Ice Silk Road.”
The cooperation between China and Russia in developing the Arctic has made positive progress. According to the introduction of China’s Ministry of Commerce in November last year, the transportation departments of the two countries are discussing the Memorandum of Understanding on Maritime Cooperation between China and Russia in Arctic Waters, and constantly improve the policy and legal basis for developing cooperation in the Arctic. In addition, the enterprises of the two countries are actively engaged in oil and gas exploration and development cooperation in the Arctic region and discussed the construction of transport infrastructure along the Arctic Passage.
Russia’s largest international energy cooperation project in the Arctic is the Yamal liquefied natural gas project, which Putin calls “a vivid example of Russia-China friendly cooperation.” As part of the end of October 2017, both China and Russia have signed a long-term sales agreement of 96.8 million tons of liquefied natural gas with a total output of 96.7 million tons. PetroChina, together with Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, China Development Bank and Silk Road Fund, completed a total of US $ 19 billion in international financing for the project, accounting for 63% of the total. Of the 142 modules required for the construction of natural gas plants, 120 were contracted by seven Chinese enterprises represented by CNOOC Marine Engineering Co., Ltd. Seven of the 30 vessels used in the construction and transport of the project are made in China and 14 of the 15 natural gas carriers are operated by Chinese companies.
According to Russian media reports, in addition to Yamal liquefied natural gas project, the Arctic region’s largest city of Arkhangelsk deepwater port reconstruction project has identified the presence of Chinese enterprises. Vladimir Lemega, a professor at the University of Finance and Economics of the Russian Federation, said that “Ice Silk Road” will become an excellent transport option for global maritime trade in the future and will power Russia’s Arctic pioneering program. The cooperation between Russia and China is indeed The key to achieving the goal.
The Nordic countries are willing to actively participate in the construction of ice silk road
Iceland, as a country in the Arctic region, has always maintained close cooperation with China on the issue of polar regions. In 2012, China and Iceland signed the Memorandum of Understanding on Scientific and Technological Cooperation between China and Iceland in the Ocean and Polar Regions, and the two sides further deepened their cooperation. The proposed “Silk Road on Ice” initiative will undoubtedly give more meaning to the cooperation between China and Iceland on the issue of polar regions.
At present, the polar cooperation between China and Iceland mainly concentrates on scientific research. The aurora observatory set up jointly by the China Polar Research Center and the Icelandic Research Center will be put into operation this year. Upon completion, scientists from China, Iceland and other countries will be accepted. The chairman of the Arctic Circle and former Icelandic President Grimsson said that China is looking forward to extending the field of scientific cooperation between China and Iceland to glaciology and new energy so as to make more contributions to humankind’s understanding of the Arctic and global challenges such as climate change.
“Ice Silk Road” will bring new opportunities for the cooperation between China and Iceland in the field of Arctic infrastructure. It is reported that China had studied the construction of a deep water port project in the northern Gulf of Iceland in order to make Iceland a major shipping center on the North Sea route. Although the port project is still under study, the level of cooperation between the two countries on the polar issue has been steadily increasing. In addition, Iceland has allowed CNOOC to explore oil in Icelandic waters and businesses in both countries are still engaging in on-site utilization of thermal energy.
As a great Arctic region, Finland is always interested in cooperating with China on the establishment of a pragmatic infrastructure in the Polar Regions. Finland welcomes China’s proposal for the “Silk Road on Ice” and hopes to promote its connection with the “Arctic Corridor” in the country so that Finland will become a pivotal country in the Arctic and Eurasia.
The planned Arctic railway will connect the Baltic Economic Zone with the Arctic deepwater port. In an interview with this reporter, Los Angeles, head of the “Arctic Corridor” project, said that the “Ice Silk Road” initiative is of great significance to Finland and the entire Arctic region. Finland is willing to become “the Silk Road on Ice “Portal countries that extend to the Nordic and Continental Europe.
Lossi believes that the extension of the “Ice Silk Road” to northern Europe will greatly increase the amount of trade and traffic between the Arctic and the Nordic countries and Finland hopes to use it to create the new global economic zone and transport development corridor. ” The Arctic Corridor opens up the “last mile” to the Nordic countries and Eastern European markets for the “Ice on the Silk Road,” connecting China with Russia to the Pan-European Transport Network.
Lothy looks forward to the “Arctic Corridor” and the “Ice Silk Road” Unicom, together to build a magnificent transportation network across Europe and Asia. Hilkaneh, Norway at the end of the “Arctic Corridor” is the nearest western port on the northeast route to Asia. Once the Arctic route reaches frequent navigations, Kirkcalf will assume an important cargo duty. Ports in northern China are also of importance Will be promoted. “Free trade and cooperation are of paramount importance to the sustainable development of the Arctic and will be a win-win cooperation between the two initiatives,” said Losy.
Finnish Arctic Center PR head Marcuseh Keeley told this reporter that as the rotating presidency of the Arctic Council, Finland actively encourages China to participate in the Arctic cooperation. At present, Finland is assessing the construction of an Arctic submarine cable to build a seabed Silk Road between Eurasia. As soon as it is completed in 2020, it is expected that this submarine fiber optic cable will become the fastest data channel to connect Europe with China.







No Comments Yet.